In the retail industry, a planogram is a visual representation of the strategic placement of products on shelves to optimize sales. Planograms play a critical role in ensuring that retail stores are visually appealing, easy to navigate and that products are displayed in a manner that attracts customers. Let’s explore the concept of planograms, provide real-world examples of planograms, and introduce effective solutions for creating and implementing planograms.
What is a Planogram?
Planograms, also known as plano, are crucial visual representations in physical retail stores. They provide a clear layout of where and how to place products on shelves or displays. Effective planograms can lead to increased sales and improved customer experience. Careful consideration of product placement and overall display appeal is essential in creating planograms that do not create clutter or confusion for customers. Regular updates to planograms are necessary to reflect changes in product assortment, new products, and seasonal trends. As such, retailers must ensure that their planograms are regularly updated and aligned with their sales and marketing strategies.
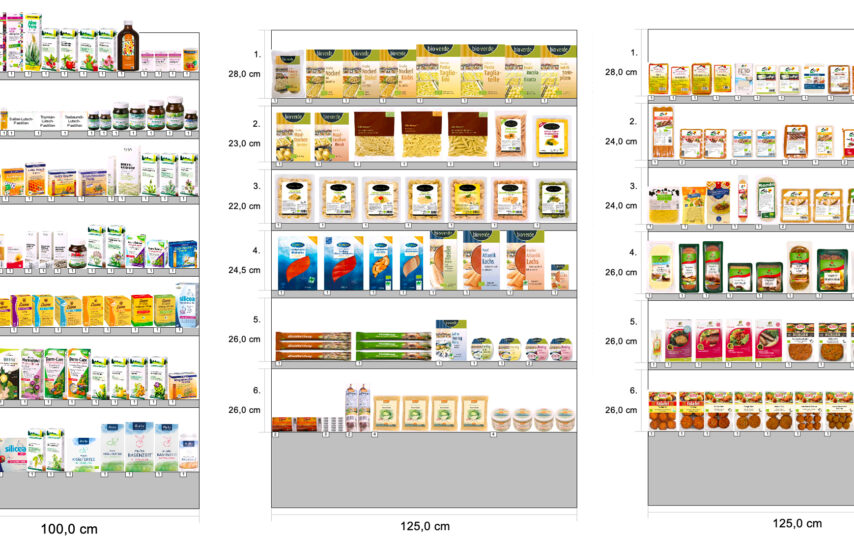
A planogram example in a grocery store
What are the types of planograms?
There are different types of planograms that retailers use to efficiently use physical space in stores and maximize customer purchases. Some of the types of planograms include product placement based on market share, margin, commercial status, and block placement. Block placement planogram involves grouping all products in a specific category in the same space. A planogram can be thought of as a schematic drawing that shows the store’s shelves and products, and includes the location of each product on the shelf.
An example of planogram software
Examples of how planograms can be used in retail
Planograms can accomplish multiple tasks at once, here are a few examples of planogram usage:
- Maximizing product visibility: Planograms enable retailers to position their products in a way that maximizes their visibility to customers. By placing high-demand or high-margin items at eye level or end caps, retailers can capture customers’ attention and increase the likelihood of purchase. This strategy can be especially effective for new or seasonal products that customers may not be familiar with.
- Cross-selling and upselling: Planograms can be designed to encourage customers to purchase complementary or related items. Retailers can place such items in close proximity, making it easy for customers to discover and purchase them together. This strategy can lead to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
- Seasonal and promotional displays: Planograms are particularly useful during seasonal and promotional periods. Retailers can use them to plan and execute displays that align with specific themes or occasions, creating an engaging shopping experience for customers. This can help retailers build brand awareness, increase customer loyalty, and drive sales.
- Category management: Planograms assist with category management by grouping similar products together. By arranging items logically and consistently, planograms make it easier for customers to find what they’re looking for, reducing search time and improving overall satisfaction. This strategy can also help retailers to optimize shelf space and minimize clutter.
- Space optimization: Planograms help retailers make the most efficient use of available space. They ensure that products are displayed in a way that minimizes clutter and maximizes capacity, leading to a more organized store layout and enhanced customer flow. This can help reduce wait times, minimize customer frustration, and increase sales.
An example of a macro space planogram
- Inventory control and replenishment: Planograms can aid in inventory control by specifying the quantity and location of each product on the shelves. This information can be used to monitor stock levels, facilitate efficient replenishment, and minimize out-of-stock situations. This strategy can also help retailers to optimize their inventory management processes and reduce waste.
- Aesthetic appeal: Planograms take into account visual aesthetics such as color coordination, symmetry, and balance. By considering these factors, retailers can create visually appealing displays that capture customers’ attention and enhance the overall ambiance of the store. This can help build brand recognition, increase customer loyalty, and drive sales.
- Store layout planning: Planograms are valuable tools when designing or modifying store layouts. They help retailers determine the most effective placement of different product categories, aisle widths, and the flow of foot traffic. Optimizing the store layout based on planograms can improve customer navigation and increase the likelihood of product discovery. This strategy can also help reduce wait times, minimize customer frustration, and increase sales.
How can planogram software simplify the creation of planograms?
With the help of planogram software, retailers can create and implement effective retail plans. By leveraging sales and space data, it can create tailored planograms that take into account a store’s layout, sales, and logistics requirements. The software supports various fixture types and provides visualization tools and planogram performance data to ease decision-making.
One of the main benefits of using planogram software is the paperless approach, which can help create attractive and profitable planograms with minimal manual input. Additionally, the software provides regularly updated reports, monitoring, and analytics for effective merchandising of business operations. With planogram analytics software, retailers can analyze and optimize the layouts they created, taking into account ABC indicators, used and available areas, and sales per square foot or meter. By doing so, the software helps optimize time and labor costs while maximizing sales per unit of space.
Conclusion
Planograms are an essential component for retail stores to enhance their visual appeal, optimize product placement, and improve the overall shopping experience. By strategically arranging products on shelves or displays, retailers can maximize visibility, encourage cross-selling and upselling, create engaging seasonal displays, facilitate category management, optimize space utilization, control inventory, and enhance the aesthetic appeal of their stores. With planogram software, retailers can create attractive and profitable programs with minimal manual input, optimize layouts based on key indicators, and maximize sales while minimizing time and labor costs. Utilizing planogram software can facilitate the optimization of product placement and merchandising strategies, thus leading to an improved shopping experience for customers and increased sales for retailers.