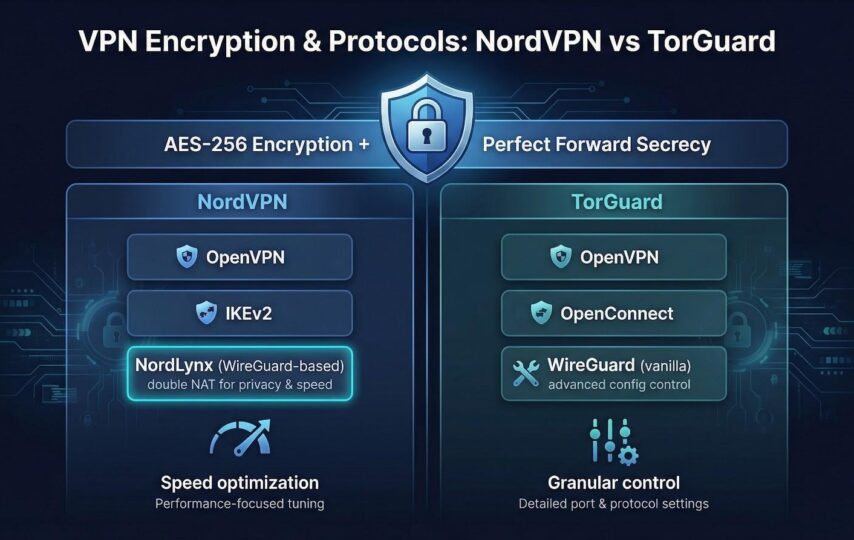
Encryption standards & VPN protocols
AES-256: the unbreakable baseline
Both NordVPN and TorGuard lock every packet behind AES-256 encryption, the cipher governments still trust for top-secret traffic. Nord pairs AES-256 with perfect forward secrecy across OpenVPN and IKEv2; TorGuard mirrors that setup. In raw cryptography, the two services give your logins the same steel vault—CyberNews’ 2025 test notes “no measurable difference in cipher strength.”
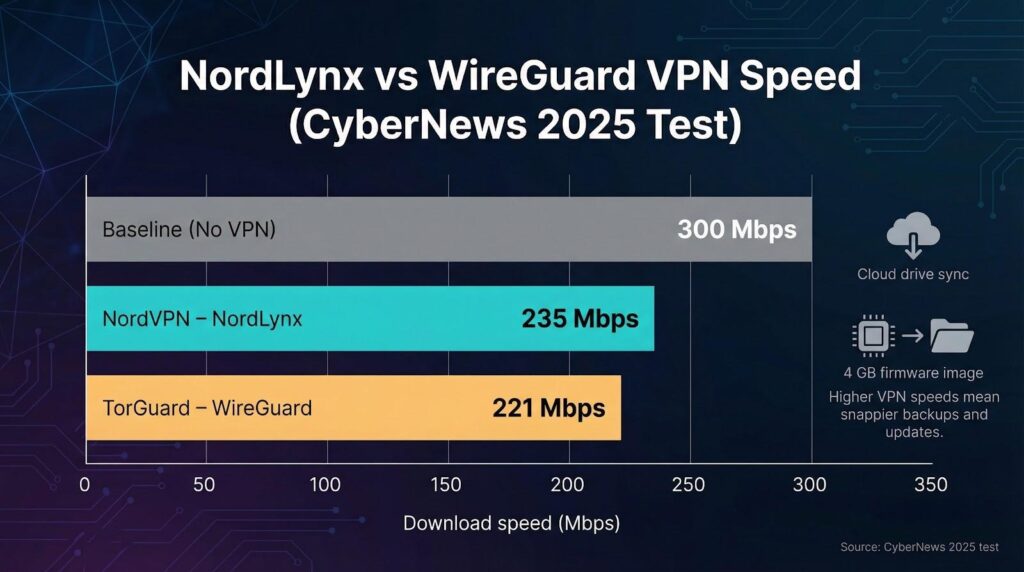
WireGuard vs. NordLynx: speed meets privacy
TorGuard ships vanilla WireGuard alongside OpenVPN and OpenConnect, so power users can tweak ports and flags. NordVPN forked WireGuard, added a double-NAT layer, and branded it NordLynx. CyberNews clocked NordLynx at 235 Mbps on a 300 Mbps line, edging out TorGuard’s 221 Mbps on stock WireGuard. You’ll feel that gap when syncing a cloud drive or pulling a 4 GB firmware image.
TorGuard’s own WireGuard setup guide shows you can generate a fresh “.conf” file in the dashboard’s WireGuard Manager, tied to any server you like.
Feed that file into wg-quick on a Fedora VPS or upload it to an OpenWrt router and the tunnel is live in under a minute—no proprietary client needed.
Performance overhead: small tweaks, big gains
Less overhead keeps bank sessions alive and video calls crisp. In Security.org’s 2025 lab run, NordVPN dropped just 5.8 percent of baseline speed; TorGuard lost 39 percent—evidence that Nord’s in-house tuning pays off.
Bottom line
Encryption strength is a draw, but NordVPN slides the vault down a sleeker rail. If you want effortless top speed, pick NordLynx; if you crave granular control, TorGuard’s protocol buffet is your playground. Either way, your data stays locked tight.
Kill-switch & leak protection
Why your VPN needs an instant off-switch
Imagine your café Wi-Fi hiccups, the tunnel drops for half a second, and every browser tab reverts to your real IP. That micro-leak is all an attacker—or a nosy website—needs to fingerprint your account.
A kill-switch stops the bleed. The moment the VPN connection falters, it cuts your device’s internet access, keeping logins, cookies, and torrent peers blind to your location. Without it, even the strongest encryption is a seat belt in a car with no doors.

Both NordVPN and TorGuard ship a kill-switch on every desktop and mobile app, yet their approaches differ:
- NordVPN hides the control behind a single toggle labeled “Kill Switch,” delivering a one-step, all-or-nothing cutoff users can trust.
- TorGuard offers three modes—system-wide block, app-specific closes, and custom scripts that fire firewall rules the instant a packet slips.
Whether you prefer simple safety or granular control, always arm this circuit breaker. In the next part of our leak deep-dive, we’ll see how each provider contains DNS traffic and prevents WebRTC slip-ups.
No-logs policy, audits & jurisdiction
TorGuard, marketing itself as the best anonymous vpn service for everyday privacy, echoes the same “we store nothing” mantra but with one important caveat.
What each provider promises on paper
Before we dive into courtrooms or audit reports, let’s start with the pledge each company makes the moment you hit “subscribe.”
NordVPN’s privacy policy is blunt: no traffic logs, no IP timestamps, not even bandwidth counters. The company runs from Panama, a country with no data-retention rules and zero membership in the Five-Eyes surveillance alliance. In plain English, Nord is not legally forced to collect your browsing trail—and it says it does not. Four independent audits since 2018 back that claim.
TorGuard echoes the same “we store nothing” mantra but with one important caveat. Its parent firm is registered in the United States, a jurisdiction famous for subpoenas and copyright crackdowns. TorGuard insists that even under pressure it has no usable records to hand over, yet it has released zero public audit results. The legal environment it lives in is unquestionably harsher.
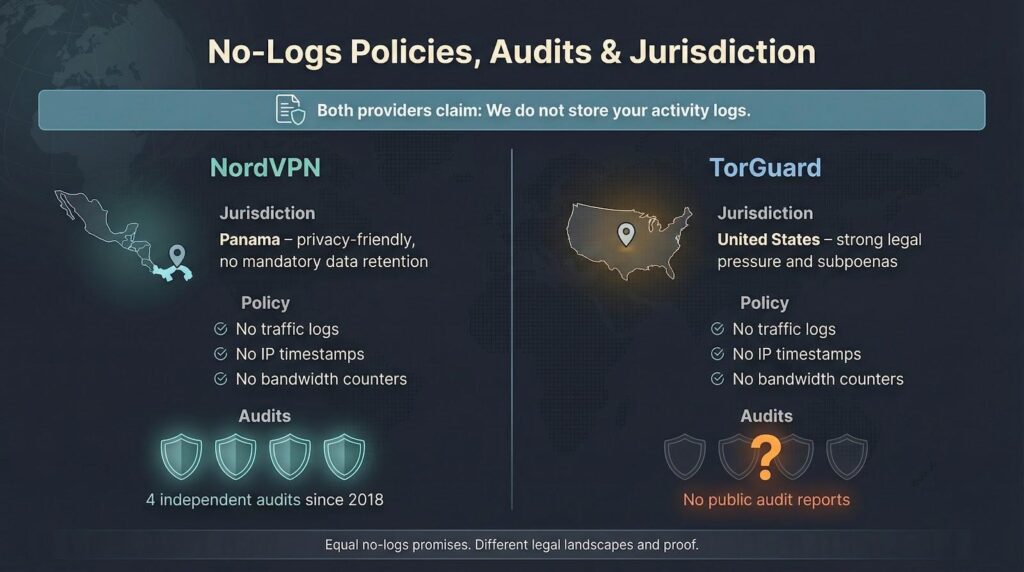
On paper, both VPNs promise equal privacy. The difference is geography: one sits in a privacy-friendly haven, the other on Uncle Sam’s front porch. In the next subsection we’ll look at which provider has proven the promise in practice.
Server network security & infrastructure
Size matters, and so does what sits under the hood
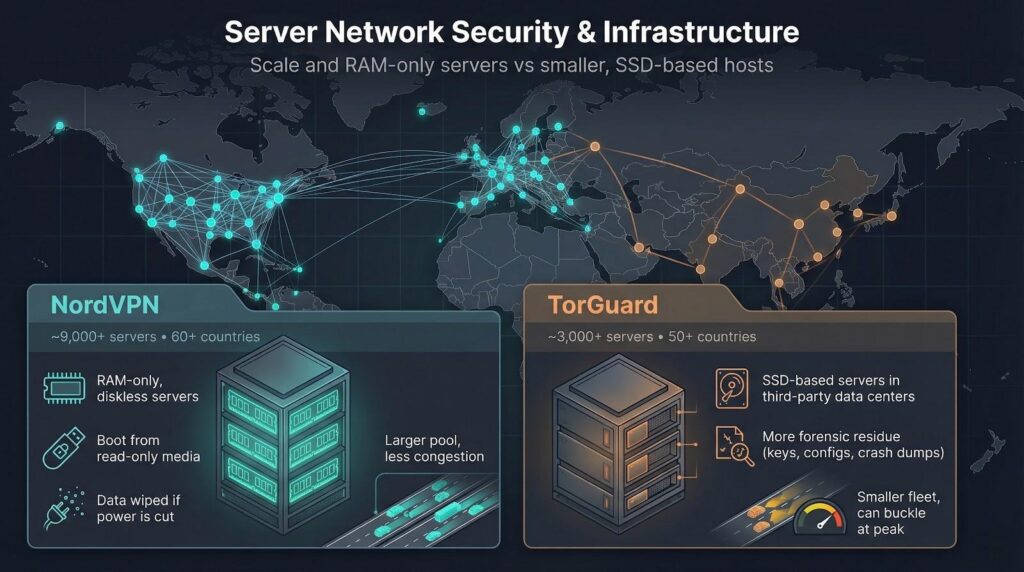
The more servers a VPN runs, the harder it is for anyone to zero in on your traffic. NordVPN leads that numbers game with about 9,000 locations in more than 60 countries. TorGuard fields roughly 3,000 in just over 50 nations. Twice the coverage lets Nord scatter your sessions across far more IP addresses, thinning any breadcrumb trail an investigator might follow.
But raw count tells only half the story. After a 2018 data-center breach, NordVPN rebuilt its fleet as RAM-only. Every server now boots from read-only media and writes nothing to disk. If someone pulls the plug, any in-memory data disappears. CyberNews calls this design “the gold standard for privacy at scale,” and it keeps account cookies from lingering on seized drives.
TorGuard has not announced a full RAM transition. Most nodes still rely on traditional SSDs managed by third-party hosts. That setup does not prove logs exist, yet it leaves more forensic crumbs—keys, configs, crash dumps—that a determined actor could capture if the hardware is seized.
For daily use, you will mainly feel this infrastructure gap as load and latency. Nord’s oversized pool rotates users away from congested nodes before speeds suffer. TorGuard’s smaller roster can buckle at peak hours, and Reddit power users often recommend hopping regions to find a less crowded exit.
Bottom line: NordVPN’s scale and diskless hardware create a network that is tougher to compromise and smoother to use. TorGuard stays functional, but it cannot match the redundancy or automatic privacy wipe built into Nord’s design.
Obfuscation & censorship circumvention
Stealth basics: why disguising VPN traffic keeps accounts reachable
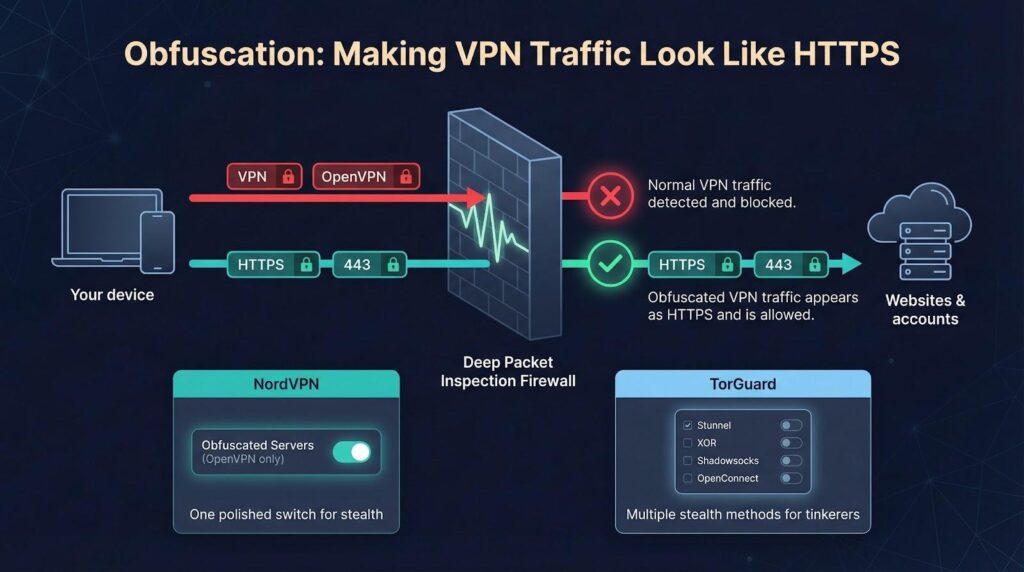
A VPN protects nothing if it cannot connect. Corporate firewalls, college campuses, and entire countries now fingerprint OpenVPN packets and block them before you even type a password. Obfuscation flips that game, wrapping VPN traffic so it looks like ordinary HTTPS. Once deep-packet inspection fails to spot the tunnel, you glide through the block and your email refreshes without a hitch.
Both NordVPN and TorGuard say they work in China, the UAE, and other tough spots, but they use different tools. Nord presents one polished switch: pick “Obfuscated Servers” (OpenVPN only) and the app moves you to nodes that scramble metadata until it blends with web noise. One setting, no extra ports, and you are browsing again.
TorGuard caters to the tinkerer. It stacks four stealth methods—OpenVPN Stunnel, XOR scrambling, Shadowsocks proxy, and Cisco-style OpenConnect. Use one, combine them, or hop ports on the fly when a network admin blocks a pattern. The trade-off is clear. Nord’s single-click stealth is simple but limited to that lone method. TorGuard’s multi-tool kit demands trial and error yet almost always finds a route.
If you work behind strict firewalls or often visit regions with heavy filtering, TorGuard’s flexibility wins this round. For travelers who just need a quick bypass at a hotel hotspot, Nord’s push-button obfuscation feels effortless.
Advanced security features
Double VPN & multi-hop tunnels
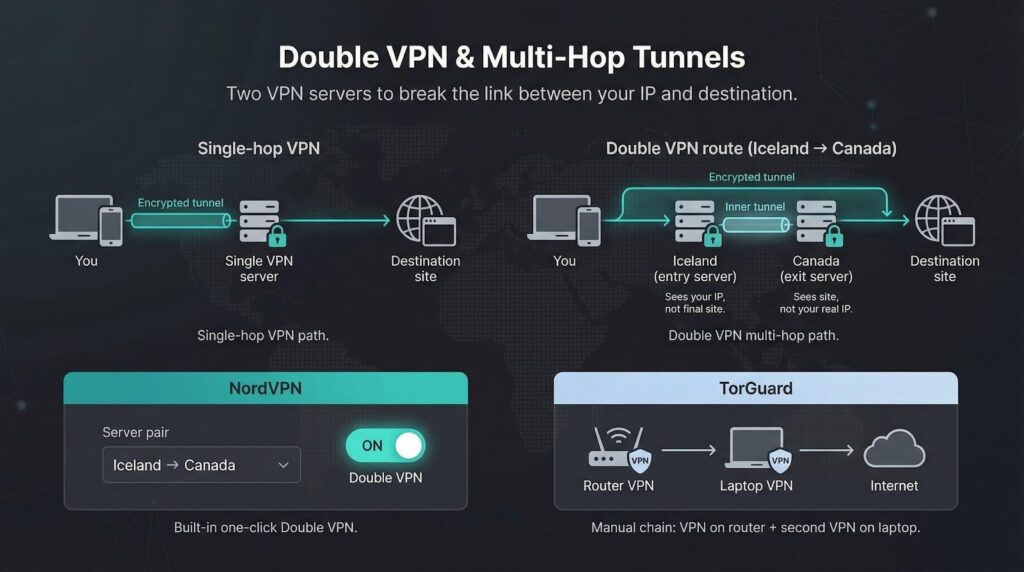
Sending your traffic through one encrypted server is good; bouncing it through two frustrates trackers and correlation attacks. NordVPN bakes this “Double VPN” option into the server list. Tap Iceland → Canada, for instance, and every packet is encrypted twice, routed through two separate data centers, then released to the internet. The extra hop trims speed by a few megabits per second, yet the payoff is clear: neither exit node alone can link your real IP to your final destination.
TorGuard skips a built-in multi-hop. You can chain it manually by running TorGuard on a router and adding a second VPN on your laptop, but that setup takes added configuration. For journalists, whistle-blowers, or anyone guarding high-stakes credentials, NordVPN’s one-click double hop is the safer, simpler choice.