In the captivating realm of science and technology, only a handful of innovations have managed to truly captivate our imagination and bring about transformational shifts across industries. Standing prominently among these innovations are 3D printers. These ingenious devices have not just revamped, but revolutionized manufacturing processes. They’ve unfurled new realms of possibilities and completely overhauled our approach to production as a whole. From the sprawling domains of aerospace and automotive industries to the intricate fields of healthcare and even fashion, the indelible impact of 3D printers is omnipresent, ushering in an era brimming with unparalleled creativity and heightened efficiency.
Understanding 3D Printing
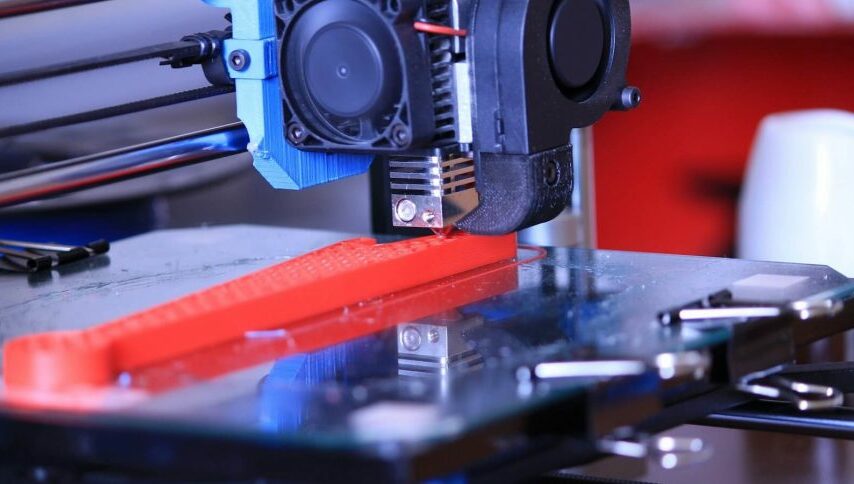
At its very essence, 3D printing, often hailed as additive manufacturing, operates as a meticulously orchestrated process, meticulously crafting three-dimensional objects, layer by layer, all meticulously derived from a digital architectural plan. This stands in stark contrast to the conventional subtractive methods that entail painstakingly carving out shapes from solid blocks of raw material. The genius of 3D printing lies in its precision – it selectively adds material exclusively where it’s needed. This not only curtails wastage to a bare minimum but also orchestrates a symphony of resource optimization, underscoring a path towards sustainability that we ardently embrace.
The Journey from Prototypes to Production
Originating in the 1980s as a tool for rapid prototyping, 3D printing was mainly utilized to craft preliminary models and prototypes. Yet, technological advancements have propelled this method far beyond its original scope. Nowadays, 3D printers possess the capability to manufacture functional components, intricate shapes, and practical items spanning diverse sectors.
Architecture and Construction: The realm of architecture and construction has also embraced 3D printing, introducing inventive resolutions for intricate designs and eco-friendly construction materials. Tasks that previously demanded months for fulfillment can now wrap up within days, thus curtailing the total expenses associated with construction.
During the initial stages of 3D printing’s development, its main application revolved around rapid prototyping. Designers and engineers could quickly create physical models of their concepts, allowing for faster iterations and improvements. This capability revolutionized product development by reducing the time and cost required for traditional prototyping methods.
Direct Digital Manufacturing:
The true turning point in the journey from prototypes to production came when 3D printing demonstrated its capacity for direct digital manufacturing. Instead of using additive manufacturing solely for prototyping and low-volume production, it became possible to create final products at scale. This opened up a world of opportunities for companies to reconsider their manufacturing strategies, eliminating the need for intermediate steps and reducing material waste.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the many benefits of 3D printing, certain challenges remain. Materials with specific properties and quality standards are still being developed. Additionally, scalability for mass production is an ongoing concern. However, research and development efforts are continuously addressing these obstacles, paving the way for an increasingly promising future.
The horizon for 3D printing appears promising, adorned with exciting possibilities like multi-material printing and applications in business and industry. As this technology advances and becomes more accessible, it stands ready to democratize manufacturing, granting small enterprises and individuals the means to materialize their concepts.
3D printing has emerged as a catalyst for change, reshaping how objects are conceived and crafted across diverse sectors. Originally designed as a tool mainly for rapid prototyping, 3D printing has undergone a significant evolution, now playing a crucial role in the production of functional components. Its capacity to bring about transformative change becomes apparent in its ability to reshape entire industries and drive forward innovation. As experts in research, engineering, and visionary thinking push the boundaries of this technology, the world eagerly awaits the upcoming wave of innovative applications that have the potential to shape our future in unimaginable ways.